
Silica is a mineral that many materials used in construction contain, such as granite, cement or sand, and it forms part of Silestone countertops for kitchens – which became fashionable years ago because, in addition to being decorative and resistant, were considered very hygienic – and which are now being talked about because of their relationship with the silicosis suffered by around 1,900 workers at the Cosentino company (in Almería), which manufactures these products.
Silicosis is a chronic disease that affects the lungs and is caused by inhaling silica particles. “These particles are deposited in the lung tissue, which produces alterations that, in the long run, can cause respiratory symptoms, such as coughing, dyspnea (sensation of lack of air) and difficulty breathing,” explains Dr. Luis Gómez Carrera, head of the Pneumology section of the La Paz University Hospital, Madrid.
Francisco Martínez Cosentino, CEO of this leading company in the kitchen countertop sector in Spain, has been accused of not informing his employees about the risks involved in handling Silestone quartz agglomerate, nor providing them with the appropriate protection measures for avoid them.
The businessman has just been sentenced to six months in prison, and has announced that he will reduce the content of silica crystals in his countertops by 40%, but there are numerous lawsuits underway against him, since between 2007 and 2019 they have been diagnosed with silicosis 1,856 of the workers who were in charge of cutting them and who, in doing so, inhaled the tiny particles that have caused this irreversible lung disease.
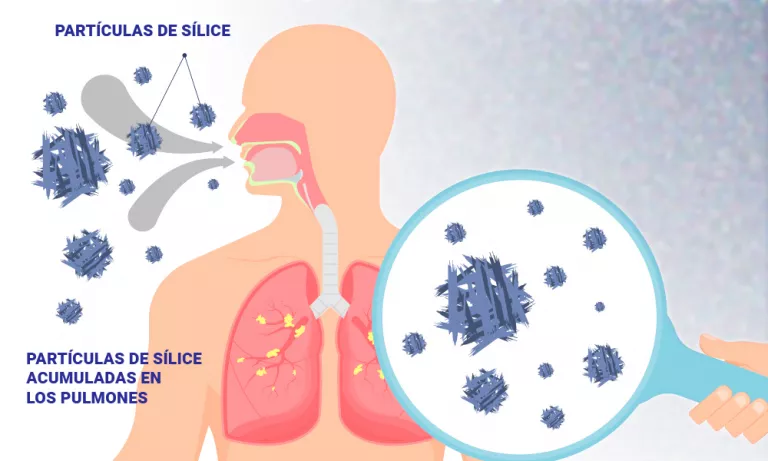
Silicosis: what is it and what are its symptoms
Most cases of silicosis are due to occupational exposure to silica, a mineral that accumulates in the lungs, where it forms fibrous nodules that deteriorate lung tissue, reduce airflow, and cause breathing difficulties. Crystalline silica is present in nature, in the earth and in certain materials, and spreads through the air when these are cut, drilled, polished or ground, forming a dust that remains in suspension – according to workers. affected – and enters through the respiratory tract.
Severe silicosis “can cause limitations in respiratory function and the ability of the lung to recover oxygen, which can lead to respiratory failure”
For this reason, the professionals most likely to develop injuries associated with this disease are those who work in sectors or industries in which materials containing silica are handled, such as quarries and mines, construction, glass and ceramic manufacturing. and sandblasting, among others.
In the specific case of Silestone countertops, the link with silicosis is due to the presence in their manufacture of a quartz compound, a mineral that contains crystalline silica. When these countertops are cut, drilled or sanded, silica particles can be released into the air, which can be inhaled and cause damage to lung tissues.
The severity of silicosis depends on the length of exposure and the number of particles inhaled during that time. In general, it takes 10 to 15 years before symptoms of the disease begin to appear, and there may be many affected who are not yet aware of it.
The workers of the Cosentino company, however, have suffered health problems more quickly – in a period of five to 10 years – because the percentage of silica contained in Silestone is very high, approximately 95%, while that of the granite is 20-30%, and that of marble is 3%.
The symptoms of silicosis are:
- persistent cough that does not go away
- Weakness, fatigue and dyspnea (feeling short of breath), especially with physical activity and which may worsen over time.
- Chest pain, especially when coughing, taking a deep breath, or exerting yourself.
- Difficulties breathing.
- Weight loss for no apparent reason.
Silicosis is also a risk factor for developing diseases such as bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), tuberculosis -especially in areas where this disease is endemic- or lung cancer. As Dr. Gómez Carrera specifies, “in the long run, the presence of silica particles in the lung may be one more risk factor for lung cancer, although silicosis does not cause lung cancer, rather it is a risk factor.” risk that, like tobacco, can contribute to its appearance”.
In any of these cases, it is important to seek medical attention if you have symptoms of silicosis, as early treatment can prevent or delay serious complications.
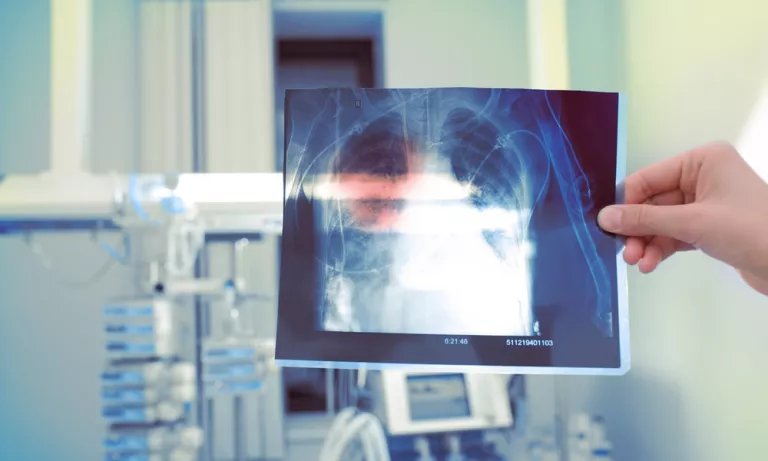
Diagnosis of silicosis
To diagnose silicosis, the doctor relies on the patient’s clinical and occupational history (his exposure to crystalline silica and the symptoms he presents) and the physical examination, together with a chest X-ray and tests to assess his lung function, such as spirometry, which measures lung capacity and helps determine if there is damage to the lungs. “Once silicosis is suspected with these tests, it would also be convenient to perform a high-resolution tomography of the chest, but for a suspected diagnosis, a chest X-ray is sufficient,” says the pulmonologist.
silicosis treatment
There is no cure for silicosis and its treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Some of the most common interventions are:
- Supportive therapies, such as administering cough and pain medications.
- Oxygen, in patients with severe silicosis who have trouble breathing and low levels of oxygen in their blood.
-
Vaccination against influenza, pneumococcus or tuberculosis to prevent these infections that could complicate silicosis.
The disease has different degrees because it depends on the time and intensity of the exposure -explains Dr. Gómez Carrera- and depending on the severity it can produce more or less alterations. “In people who have been exposed for a longer time and in whom the disease is more severe, it can cause limitations in respiratory function and the ability of the lung to recover oxygen, which can lead to respiratory failure.”
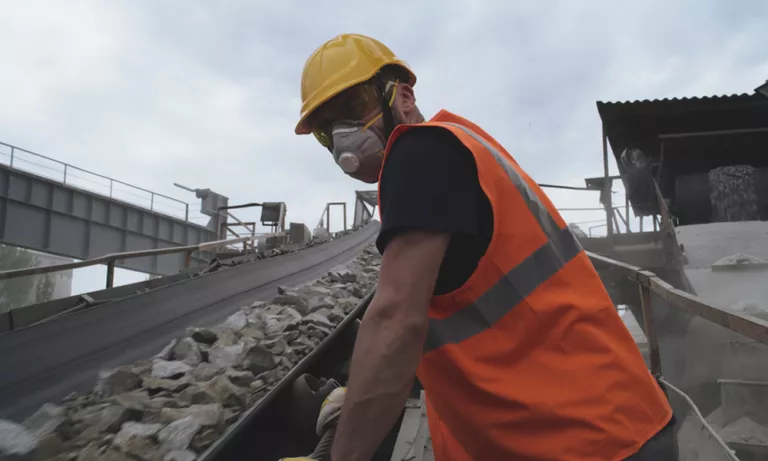

Measures to prevent silicosis
Silicosis is an incurable disease, but the good news is that it can be prevented. “To try to prevent silicosis from occurring, workers who are exposed to risk must carry out these jobs with individual protection equipment, mainly with special masks to avoid inhaling silica particles, and must follow medical controls with their health services. prevention of occupational risks routinely from time to time to check if the work is causing them silicosis and to what degree, and to stop doing that type of work if necessary”.
Other measures that help prevent silicosis in workers are:
- Adequate ventilation and cleanliness of the workplace to minimize the amount of dust in the air.
- Information and training for workers so that they can avoid the risks associated with exposure to crystalline silica.
- Use cutting, drilling, or grinding techniques that reduce the release of silica particles.
- Replace the most polluting materials with safer ones to reduce exposure to crystalline silica.
- Take measures to protect the health of workers such as those mentioned above, but also of the people who live near the work areas.
.