Having a small first-aid kit at home with basic products is key to dealing with any unforeseen event, especially if you have children at home, and avoiding unnecessary visits to the health center. One of the products that has been occupying space in this little disaster drawer for years and years is Cristalmina®, a topical antiseptic to disinfect small wounds or minor burns that are unavoidable on a daily basis. Although it is convenient to be careful, because its use is not always recommended. Keep reading and discover when and when not to resort to Cristalmina.
What is Cristalmina® and what is it for?
Cristalmina® (10 mg/ml) is a drug for topical use that is sold in Spain without a prescription, and whose active ingredient is chlorhexidine digluconate. Surely this compound sounds like you’ve seen it in mouthwashes, and it’s true, but the difference with the topical one is that the oral one is much less concentrated. As Marina Peláez Agudo, member of the Patient and Citizenship Group of the Spanish Society of Primary Care Pharmacists (SEFAP), tells us, chlorhexidine is included in the Model List of Essential Medicines published by the World Health Organization (WHO). ).
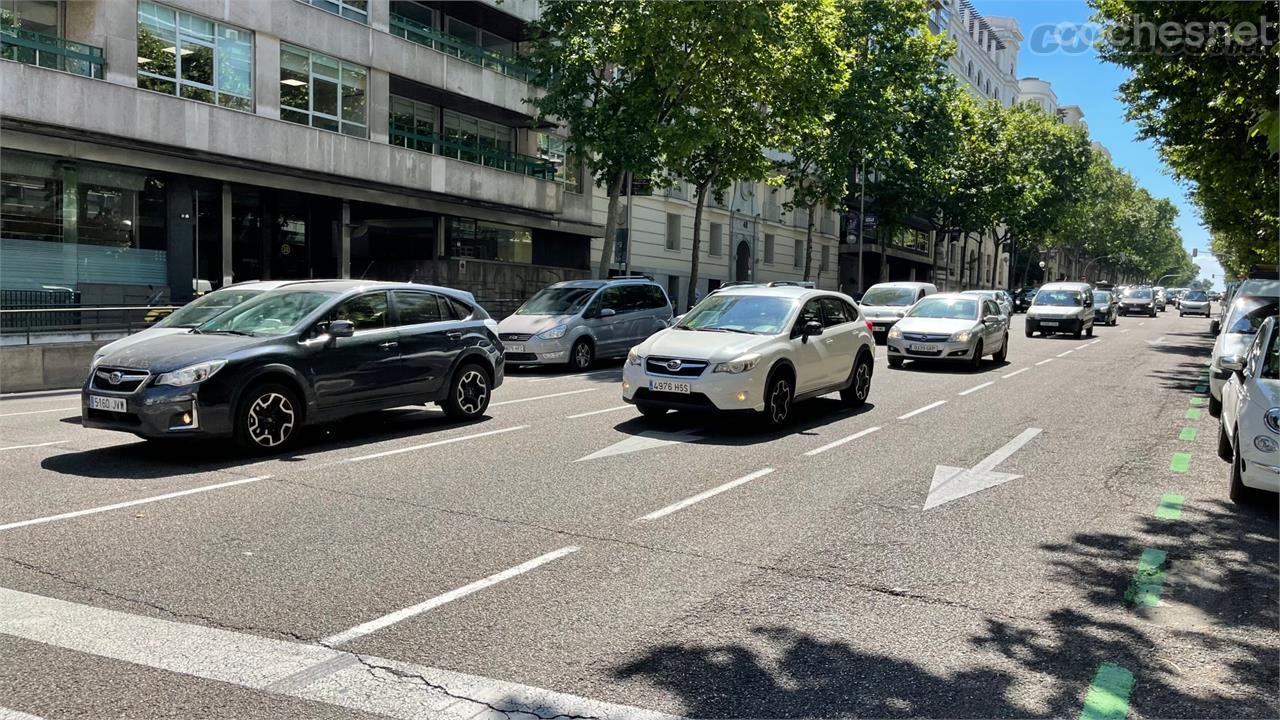
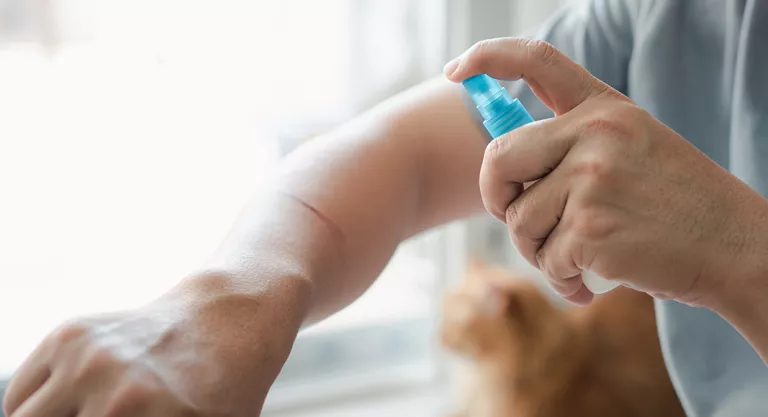
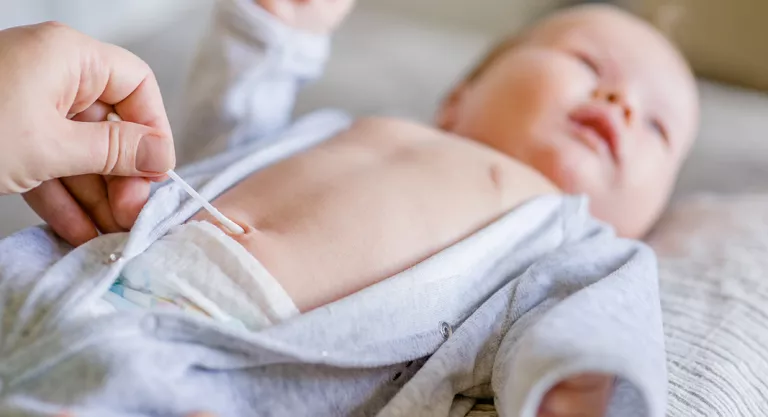
Specifically, “chlorhexidine is one of the best antiseptics available, as it has a fast and long-lasting effect, is active against numerous microorganisms (broad spectrum) and is not absorbed through the skin,” explains Cristina Fernández Marcos, from the Drug Information area of the General Council of Pharmacists. Hence its usefulness as an antiseptic for wounds, superficial cuts and minor skin burns and as an antiseptic for the navel in newborns.

One of its main characteristics is that it acts very quickly, thus, the time it takes for this product to take effect is 15 seconds after its application, and its protection can last up to six hours. In addition, it continues to disinfect even if there is soap, organic matter or blood, so it can be used on intact skin or open wounds, although it will depend on the concentration. For this reason, it is frequently used in health centers and hospitals, because it is safe in pregnant women and children.
On the other hand, it is colorless and does not stain, which prevents accidents and allows the wound to be seen at all times to see its evolution – unlike iodine, which stains the skin and can make it difficult to monitor this process. In addition, it does not sting or sting, making it a very comfortable and effective way to disinfect wounds.
Cristalmina is useful for disinfecting small wounds and burns, it can be used in children, it is colorless and acts in just 15 seconds
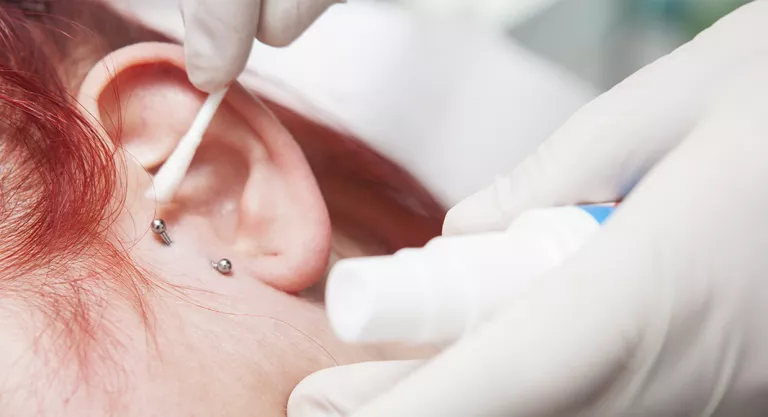
Cristalmina® 1% is considered a medicine, so it cannot be found in supermarkets or parapharmacies, only in pharmacies. Generally, it is found in the form of a spray, such as a skin spray solution, but it is also sold in dropper format, more useful for disinfecting areas of piercings, minor punctures, blisters, depilatory treatments, pet bites… In addition, there is a film format (with allantoin that re-epithelizes and hydrates the skin), which is used for domestic burns and even after suffering from insect or jellyfish stings.
Uses of Cristalmina®
As we have already said, Cristalmina® (10 mg/ml) is an antiseptic that prevents possible infections by bacteria and fungi, and can be found in different concentrations and pharmaceutical forms (spray, film or dropper) depending on its indication. In general, it can be said that this product, with a concentration of 1% chlorhexidine digluconate, is used to disinfect:
Cristalmina can also be marketed for hospital use, it is the one with concentrations of chlorhexidine digluconate at 2% or 5%, these cannot be used on open, deep or extensive wounds, they can only be applied on completely healthy skin. Its most common uses are:
Above concentrations of 5%, they are only used as disinfectants for laboratory material or hands, although their use is infrequent.
How Cristalmina® is applied
Marina Peláez Agudo explained to Webconsultas that Cristalmina® “is for topical use, it should not be ingested. It is applied once or twice a day, no more than two applications per day. In the case of topical chlorhexidine, it should be used undiluted, it is advisable to clean (with water and neutral soap or serum) and dry the wound before applying the medicine and do it directly on the affected area or on a gauze pad. Once applied, it should be left to act and dry.
Cristalmina should not be applied to the eyes or ears and care must be taken not to ingest it.
For her part, Cristina Fernández, from the General Council of Pharmacists, insists on clarifying that in 1% presentations it should be applied undiluted on the surface to be disinfected, recommending no more than two applications a day. In addition, to disinfect the hands of health personnel, it would be necessary to pour about 5 ml on the hands, rinse with water and repeat the operation again.
When to avoid the use of Cristalmina®
Chlorhexidine should not be ingested in any case, in addition, it should not be applied to the eyes or ears, or the inside of the mouth or mucous membranes, therefore, in the case of accidental contact with these parts of the body, it is recommended to wash immediately with plenty of water.
As can be read in its package insert, of course, “it is contraindicated in anyone with hypersensitivity or allergy to the active ingredient (chlorhexidine digluconate) or to any of the excipients that can be found described in the product’s package insert.”
In addition, “it should not be used in combination or after the application of anionic soaps, iodine (Betadine®), heavy metal salts or acids,” explains Marina Peláez. The SEFAP member also clarifies that “topical chlorhexidine should not be used in case of deep and extensive wounds.”
The use in children under 30 months, he adds, “will be carried out exclusively under medical supervision”, taking special care with neonates and premature babies.
According to the Cristalmina® data sheet of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS), “there are no or limited data regarding the use of chlorhexidine in pregnant women. Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity and it is not known whether chlorhexidine or any of its metabolites is excreted in human milk. However, the well-known e-lactation website qualifies Cristalmina as safe, compatible, with minimal risk for breastfeeding and the infant.
Cristina Fernández adds that among the possible rare side effects of the use of this common antiseptic are dermatitis, skin irritation, itching or photosensitivity, and warns that if any of these symptoms are observed, treatment should be discontinued immediately.
What to use on a wound or burn?
Alcohol, povidone-iodine or Betadine®, chlorhexidine or Cristalmina®, Mercromina or merbromine, hydrogen peroxide, would you know what product to use to disinfect wounds and burns?
The first thing to clarify is that the terms disinfectant and antiseptic are normally used indiscriminately, however, they are not the same. According to Nekane Bilbao, a pharmacist specializing in Hospital Pharmacy, “an antiseptic is a substance that inhibits the growth or destroys microorganisms on living tissue. The disinfectant is a compound that exerts the same action (inhibit the growth or destroy microorganisms) on surfaces or inanimate objects.
Based on this, it must be said that the use of ethyl alcohol or hydrogen peroxide is not recommended to disinfect small wounds and burns, as it irritates and damages healthy skin, in addition, alcohol is effective for bacteria, but it is not very effective against fungi and viruses. For its part, hydrogen peroxide does not work because the catalase enzyme in the skin is able to break it down quickly, so it has a slight effect on microorganisms.
Surely it sounds like you have seen the bottle of Mercromina – whose active ingredient is merbromine – at your grandparents’ house, however, its use is discouraged because it contains large amounts of mercury and because its reddish color can prevent clearly observing the progress of wound healing.
We would only be left with the options of povidone-iodine –known by the trademark Betadine®– and chlorhexidine –also called Cristalmina®–. The first one contains iodine, which is effective against many microorganisms, such as Gram+ and Gram- bacteria, fungi, protozoa, viruses and spores. This product can be used to disinfect small burns, wounds or grazes, but it should not be applied to people with thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, those who are being treated with lithium (bipolar disorder), children or pregnant women. . On the other hand, it has the same problem as mercromine, which is that it not only stains clothes or skin, but also prevents the evolution of the wound from being observed. On the other hand, the product ceases to be effective when it dries.
On the contrary, Cristalmina, as it does not stain, allows you to see how wound healing is progressing, it is fast-acting and also adheres to the skin and maintains its activity for more than 3 hours, and is very easy to apply.
.






