When we buy a computer, it is likely that Intel is in charge of manufacturing its processor. Surely you have seen it many times in the specifications of one of them or even on the sticker of your laptop. Intel i3, Intel i5, Intel i7, Intel i9… What are the differences between these processors? Which one should we choose?
In the next few paragraphs you will not find a technical and exact analysis of the differences in Intel processors in each generation, but rather a simple and easy-to-understand comparison so that you understand the differences when choosing one processor or another in a new computer that you also buy. of the factors that we must take into account to differentiate them regardless of their generation or the nomenclature that the processors of this manufacturer follow.
Nomenclature and identification of processors
The numbering tells us, if we use common sense, that the higher the number in the Intel Core i processor, the better it will be. But why and what differentiates them? It is an own or specific numbering of Intel to name its ranges and we must take into account that it has nothing to do with a technical characteristic of them nor does it talk about the cores, etc. The higher the number, of course, the higher the speed and the higher the power… But there are other numbers beyond an Intel Core i9 chip or, what is the same, not all of them are the same because the generation will vary…
There are multiple digits in the Intel Core processor. The first indicates the generation of the chip and those that accompany it are the digits that indicate the reference number and that it is used internally. In addition, there are other letters that can accompany the chip and that indicate some special characteristics. For example, if you see that a processor is an Intel Core i9 12900K it will not be similar to an Intel Core i9 10900KF.

Although the letters and suffixes may change, the endings are:
-
H – Intel high-performance graphics card included in the chip intended for laptops that are generally gaming equipment.
-
HK – Similar to H processors but overclocked
-
K – Processor unlocked for overclocking.
-
KS – K processors with higher Boost frequency
-
KF – Overclockable processors without integrated graphics
-
Q – Four physical cores.
-
T – The T corresponds to processors optimized for desktop processors, very low power processors
-
X – Dedicated to higher performance HEDT processors
-
XE – A chip dedicated to HEDT performance processors but also have the Intel certification of “Extreme Edition”
-
XS – Special HEDT processors with eight cores and whose frequency is 5.0 GHz in some of the cores, although the XS will hardly be seen among Intel processors
-
U – Low power, typically found in ultrabooks and tablets, slower than laptop chips.
-
Y – Low power, designed for low-power mobiles and laptops.
Differences between i3, i5, i7 and i9 processors
There are a number of differences between Intel Core i3, i5, i7 or i9 processors and that we must take into account and understand when choosing one or the other. The most visible thing we will see is the price. There is a logical difference between choosing one or the other. But there are also other differences such as the number of cores of each unit, the frequency, the cache memory or the power of the graphics card integrated in them.
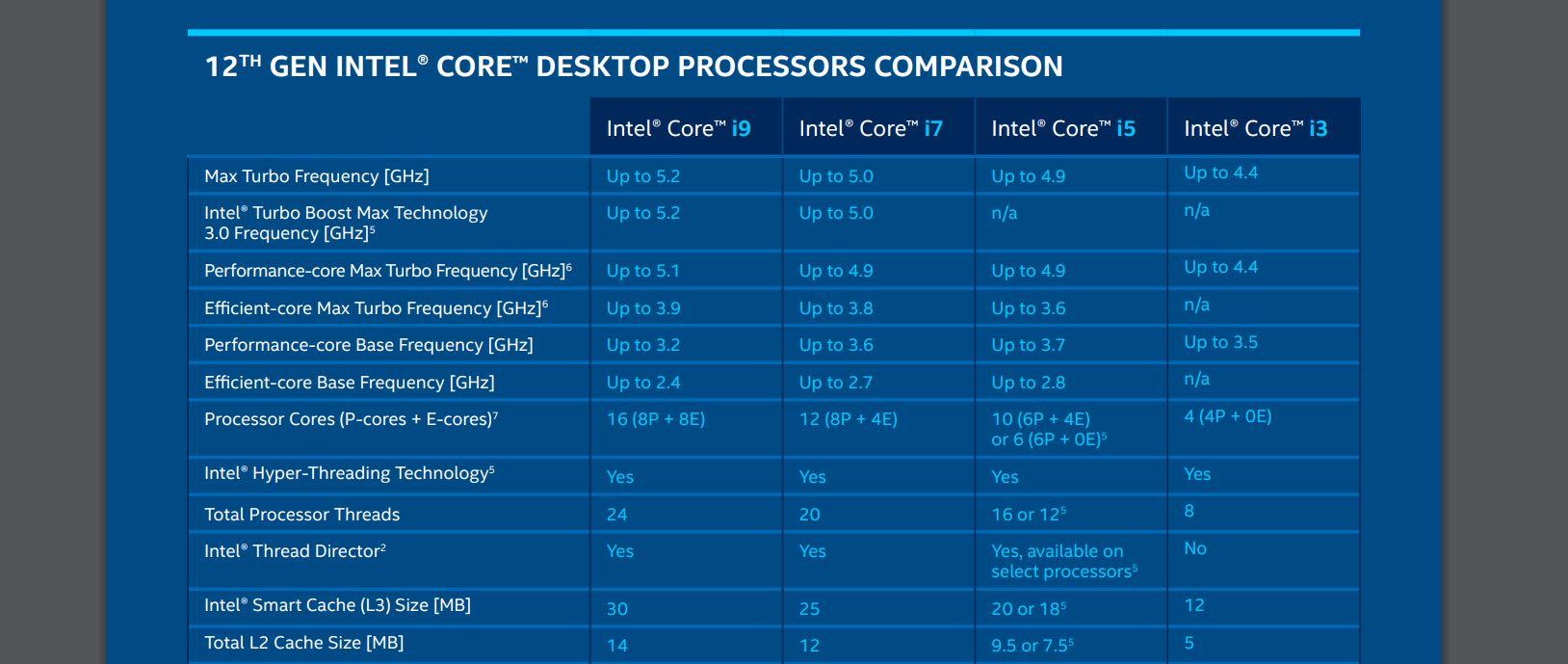
The number of cores is one of the factors that we must look at. In any generation of Intel processors, we have had at least two cores for more than a decade, but the new generations include two different types of cores: performance cores, op cores, or efficiency cores, or e cores. According to the data of the 12th generation of Intel Core, the i9 has a total of 16 cores compared to the 16 cores of the i7, the 10 of the i5 and the 4 cores of the i3. The more cores the processor has, the more tasks it can perform at once.

Another aspect that we must take into account is that of the cache memory of the processor itself, where the data that the processor needs constantly is stored and that will generally be linked to its power. In the complete comparison table between processors that you can consult in the next paragraphs, we can see the difference between the MB of cache memory of each one, including L, L2 and L3 in more modern processors.
In addition, there are other aspects that we must take into account, such as HyperThreading or a technology that divides a physical core into two logical cores or threads. This allows Intel processors for a dual-core processor to function as a quad-core, for example, and so on. Although a physical core is more powerful than a virtual one, it is another of the most important aspects.

Also the frequency of the processor is important (the number of clock cycles that a processor can perform in one second) or, related to this, the Turbo Boost function that allows the processor to go up in frequency for a certain amount of time if necessary .
Other Intel processors
The fact that it is most common to find some of the series mentioned does not mean that they are the only ones. There are others focused on having an affordable CPU and we can also find more information about them from the manufacturer’s website. This is the case of Intel Pentium or Intel Celeron in addition to Intel Atom, CPUs designed for mobile devices and IoT. Both Intel Prentium and Intel Celeron are intended for laptops or basic desktop computers.
Intel defines its Intel Celeron processors to “deliver affordable CPU performance for entry-level laptops and desktops, support strong connectivity, battery life.” They are the simplest processors in terms of power and lower than the manufacturer’s “Core” brand.

For its part, on Intel Pentium processors, the manufacturer offers “combination of speed, power and value, for daily computing in laptops, convertibles, desktops and mini PCs”. They are intended for basic equipment. We also find them in desktop computers or miniPCs and it is the simple and accessible family for equipment that is not high-end but offers just enough.
How to check all the features and differences
If we want to go a step further and consult all the technical characteristics of each of the processors of the latest Intel generations, we can do so from the website where we will download an explanatory PDF that gives us access to a table in which we will see what it has each of them, what functions includes an Intel Core i9, Intel Core i7, Intel Core i5, Intel Core i3 processor. What can we do with each of them, what does it give us compared to the others…
The first thing we need to consider is the generation of the processor we want to compare and compare processors of the same generation. I mean, let’s go to Intel website support page and from here we will go to the “Intel Core Processors” section. A periodically revised and updated version allows us to know the differences between all of them according to the generation to which they belong from the 6th generation of Intel processors onwards.
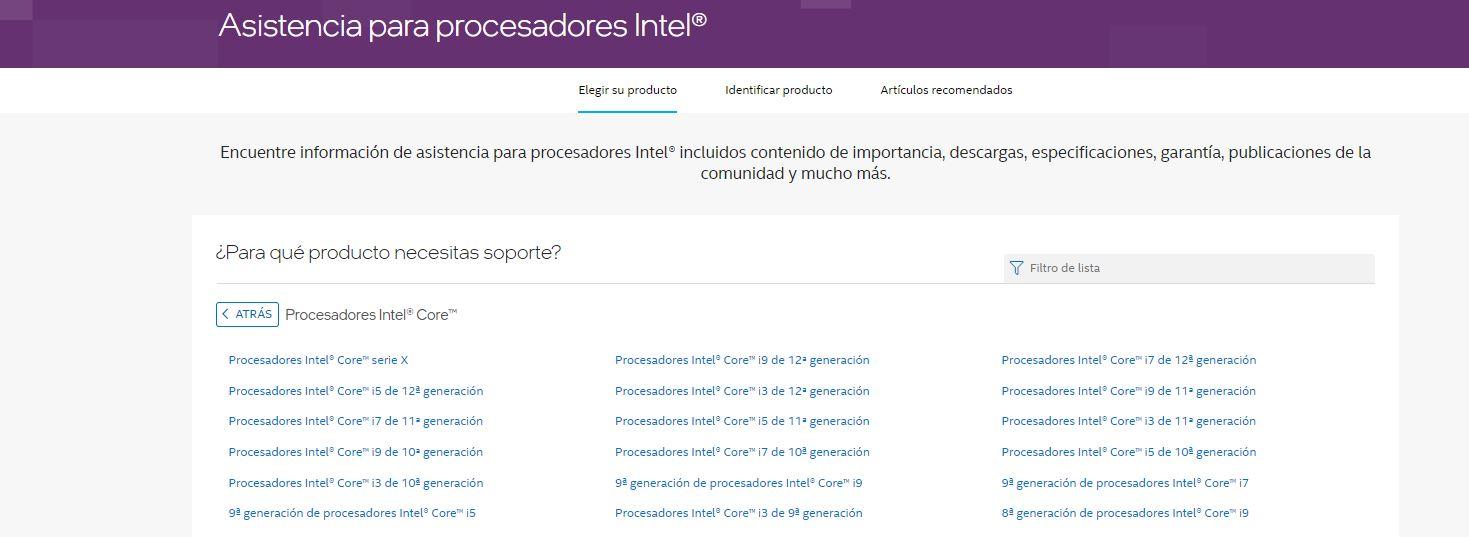
Just tap on the link and download the corresponding PDF, like the one you see on the screenshot below, where we will see the detailed comparison. This can be especially useful if you’re looking for something concrete, if you’re wondering something specific. For example, which processors have Intel Thread Director? It is a hardware solution for the optimal programming of tasks that maximizes the performance of the 12th generation of Intel processors, but not all of them have this function and from the comparative table we can clear up any doubts.