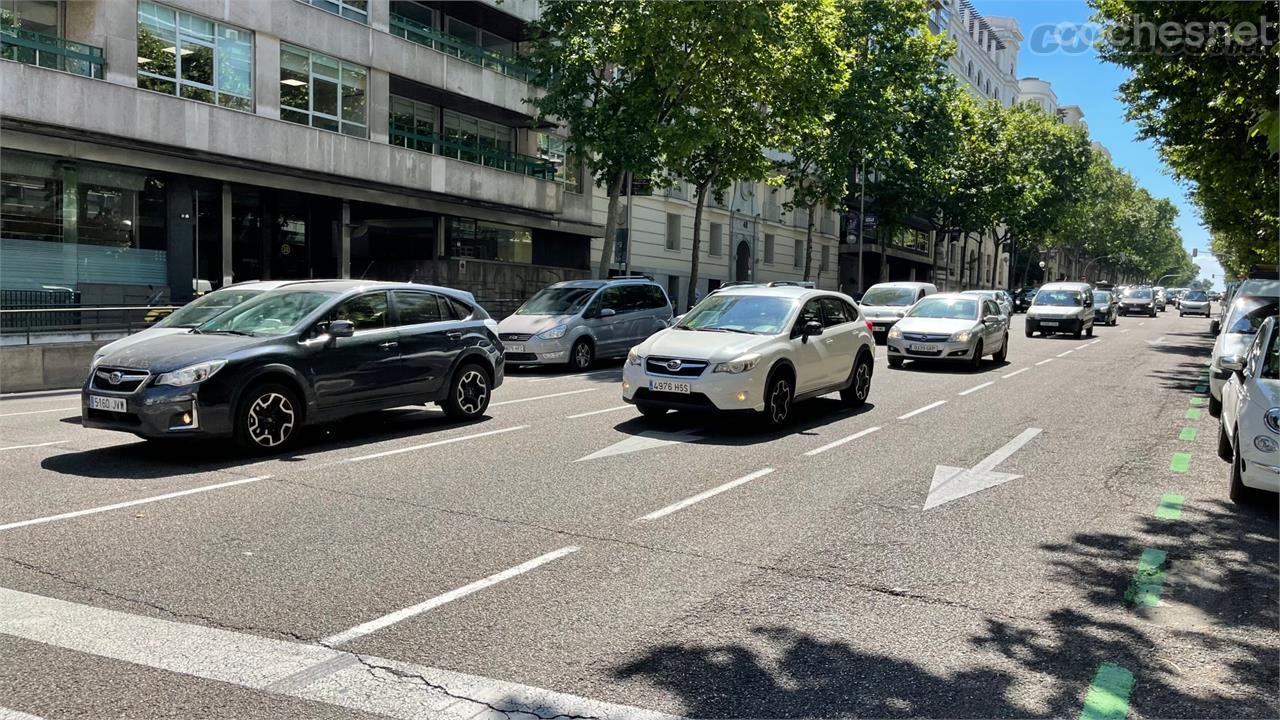
What is ophthalmic prophylaxis of the newborn
In cases of very close relatives or of our own baby, we have been able to observe that the newborn, when leaving the delivery room, has his eyes impregnated with a somewhat sticky yellowish substance. It is “an erythromycin or tetracycline ointment, which is applied after childbirth, since it is very important to do ophthalmic prophylaxis against possible infections by sexually transmitted microorganisms from the mother, which can prevent conjunctivitis with serious local consequences in the eyes. , and even systemic”, explains Gracia Peña, ophthalmologist of the IHP Group (Hispalense Institute of Pediatrics).
This neonatal conjunctivitis can be acquired by microorganisms such as gonorrhea or chlamydia (or even by viruses such as genital herpes, although it is much less frequent), which are in the birth canal; but it can also be caused by direct contamination, so ocular prophylaxis must also be used if the birth was by caesarean section. And it is that although in women sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea or chlamydia can be asymptomatic, in the baby they can lead to many complications.
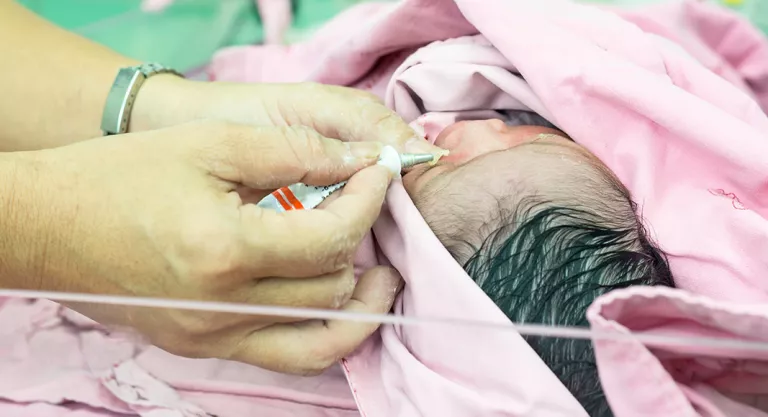
In short, with an antibiotic solution applied topically to both eyes and in a single dose, which is painless for the little one, serious problems can be avoided. In fact, it is a recommendation supported by the entire medical community at the international level, and indicated by the World Health Organization.
How Neonatal Ocular Prophylaxis Is Performed
Regarding this prophylaxis of the newborn’s eyes, we can take into account the following considerations:
What is neonatal conjunctivitis and what causes it
The newborn can present conjunctivitis (mainly in the first four weeks of life, although it usually appears between the second and fifth day after birth) due to various causes such as obstruction of the tear ducts or irritation. But if it is caused by infectious causes, the ophthalmologist of the IHP Group (Hispalense Institute of Pediatrics) Gracia Peña points out that “quick action with pediatric intervention is required.”
This clinical picture is characterized by an inflammation of the eyeball, with watery or purulent secretions, which can present complications and trigger permanent eye damage, or even blindness.
As specified by the Vall d’Hebron hospital in its protocol for the diagnosis and treatment of neonatal conjunctivitis of 2019 “Currently, in developed countries Chlamydia trachomatis is the most frequent agent of neonatal conjunctivitis (2-40% of neonatal conjunctivitis)” . Other bacteria are also the cause (30-50% of cases) such as Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus or Escherichia coli”. Of course, these experts state that “the prevalence of neonatal conjunctivitis by Neisseria gonorrhoeae has decreased drastically since the establishment of prophylactic measures in industrialized countries.”
Thus, the prognosis and treatment will vary depending on the causative infectious agent. Of course, you always have to maintain a lot of hygiene to avoid contagion in the little one.
.





