A team of cybersecurity researchers from the University of Florida (United States) has discovered vulnerabilities in some wireless induction (Qi) charging systems. As explained in their study, published on the arXiv.org platform, commands could be sent to overheat these devices and damage smartphones that were charging.
The type of attack, which they have called VoltShcemer, consists of sending “inaudible” commands to the voice assistant of smart Qi standard chargers. Specifically, the researchers say that a cybercriminal could ask the charger to perform a series of actions to the point of overheating and ending up damaging the phones or other devices that were being used.
How was an iQ wireless charger hacked?
In the study, experts clarify that the vulnerability is due to the fact that iQ-type wireless chargers use a magnetic field that connects the charger and the phone (or other device) to enable battery charging. This makes them susceptible to intentional electromagnetic interference, something they took advantage of in their experiment.
Currently, wireless induction chargers do not use an encrypted communication protocol to be compatible with all devices enabled for this type of charging. In this way, manufacturers ensure that anyone can use them comfortably, without having to pair or configure them.
As clarified in the investigation, by not using an encrypted protocol, the commands are transmitted in plain text, which makes them more vulnerable. The University of Florida team tried to intercept the communication between the charger and the phone by developing a ‘rogue’ power adapter.

With the plug manipulated, the research group says in their study that they were able to send commands to a total of nine models of iQ chargers and block the messages that it sent to the phone.
After discovering the vulnerability in the charger, the researchers attempted to transmit silent voice commands through the mobile’s built-in voice assistant. This technique was possible because they managed to get the smartphone’s microphone to convert sound into electrical vibrations, allowing settings to be changed without anyone noticing.
Why does the phone overheat?
Generally, when a modern mobile phone reaches 100% of its battery, the charger stops its charging process. This prevents overheating and energy waste. However, the researchers were able to send commands that forced the devices to continue charging.
This caused the chargers to overheat and the same thing to happen with the smartphones. In fact, experts say that 81ºC (178ºF) was reached on a phone.
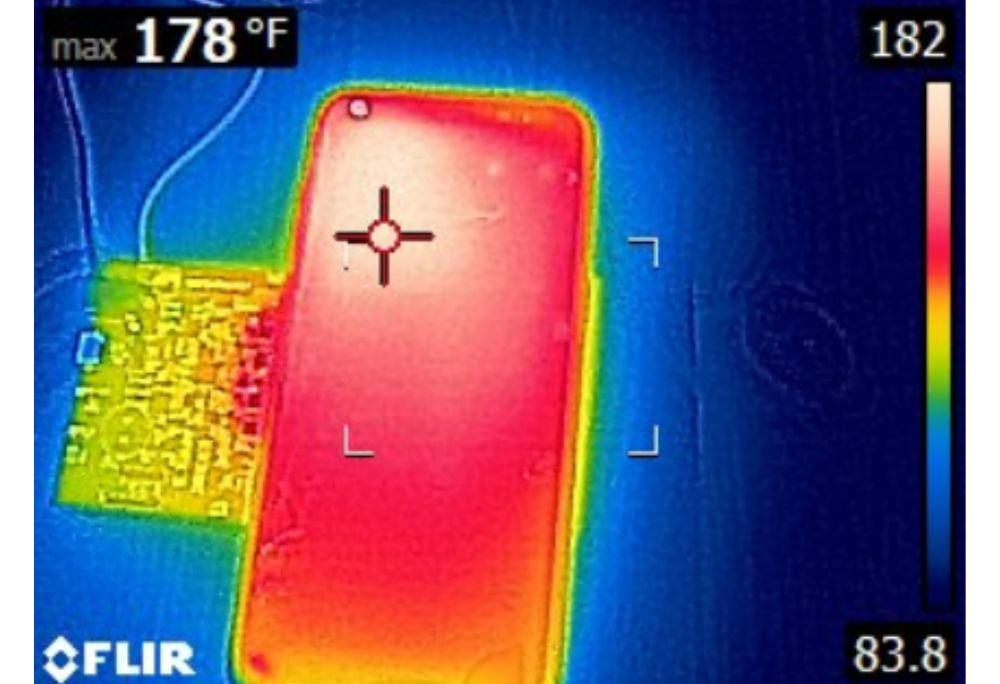
Furthermore, in the study, they put other elements on the hacked wireless chargers and discovered that this temperature could be exceeded. During the experiment, they placed bank cards, biometric passports, car keys, a USB flash drive and a paper clip. This last object reached 280 degrees Celsius.
A wireless charger is safer than a regular one
The technology that uses wireless charging is increasingly more practical and safer than conventional charging methods. Thanks to these devices, experts explain that the introduction of malware can be avoided with techniques such as ‘Juice Jacking’, known for hiding through USB ports.
Despite making ‘Juice Jacking’ attacks impossible, we now know, thanks to Florida researchers, that vulnerabilities still exist that still need to be fixed. In this situation, experts recommend taking extreme precautions and not using a standard iQ wireless charger charging in public places, since they could change the charging adapter for a tampered one.
Likewise, researchers advise not leaving your phone charging for more than an hour at a time on a standard iQ wireless charger.













